|
Ancient Asian
|
|
 |
|
 |
|

Price :
Contact Dealer
The T’ang Dynasty was an era of unrivalled wealth and luxury. The country was successfully reunified and the borders were expanded, pushing Chinese influence into new More »
The T’ang Dynasty was an era of unrivalled wealth and luxury. The country was successfully reunified and the borders were expanded, pushing Chinese influence into new lands. Confucianism became a semi-religious instrument of the state; yet Buddhism continued to flourish, spreading into Korea and Japan. The arts reached new levels of sophistication. Poetry and literature flourished under the enlightened rulers. The Silk Road brought fortunes into China. Precious treasures were imported on the backs of camels from far away lands and bartered for Chinese silk, medicinal herbs, and pungent spices. T’ang China was a multicultural empire where foreign merchants from across Central Asia and the Middle East settled in the urban centers, foremost among them the thriving capital of Chang’an (modern X’ian), a bustling cosmopolitan center of over two million inhabitants. Foreign traders lived next to native artisans and both thrived. New ideas and exotic artistic forms followed alongside. The T’ang Dynasty was a cultural renaissance where many of the forms and objects we now associate with China were first created. Moreover, this period represents one of the greatest cultural outpourings in human history.During the T’ang Dynasty, sculptural effigies of domesticated animals were often interred in the tombs of nobility and elite members of the social hierarchy. Created in all media, these sculptures accompanied the spirit of the deceased into the afterlife. While similar examples exist, most were found harnessed to wagons and carts and were meant to function as beasts of burden. However, this sculpture was discovered buried as part of a herd, contained inside a sculpted miniature pen with other domesticated animals, suggesting that this ox served as nourishment. Besides it function, this sculpture is also remarkable for its size and exquisite state of preservation, horns and ears intact. Some of the original red pigment that once decorated the animal is also visible on its nose and mouth, as well as its hooves. During the T’ang Dynasty, the Chinese believed that the afterlife was a continuation of our earthly existence. Thus, logically, as we require food to nourish our bodies on earth, so too will we require food to nourish our souls in the afterlife. Created to serve as food for the afterlife, this work is more than a mere sculpture; it is a gorgeous memorial to the religious and philosophical beliefs of the T’ang Dynasty. This cow effigy has served its eternal purpose well. Today, it continues to nourish our souls with its beauty and grace. - (H.878) « Less
|
|
Ancient Asian
|
|
|
|
|
| Vendor Details |
Close |
| Contact Info : |
| Barakat Gallery |
| 405 North Rodeo Drive |
| Beverly Hills |
| California-90210 |
| USA |
| Email : barakat@barakatgallery.com |
| Phone : 310.859.8408 |
|
|
|
|
|
|

Price :
Contact Dealer
The Yuan Dynasty was established by Kublai Khan, the grandson of Genghis Khan, upon relocating the capital of his empire from Mongolia to Beijing. The Forbidden City was More »
The Yuan Dynasty was established by Kublai Khan, the grandson of Genghis Khan, upon relocating the capital of his empire from Mongolia to Beijing. The Forbidden City was constructed, a relative oasis of Mongolian culture in the heart of China. While the Mongol elite retained their native language and customs, they did adapt the Chinese system of bureaucratic government and cemented the authoritarian rule of the emperor. Although they were unaffected by Chinese culture, the Yuan did little to stifle the native traditions and beliefs of their subjects. Buddhism continued to flourish, although the monasteries received little funding from the state. In fact, during the Yuan Dynasty, China first began to open up to foreigners. Christian and Hindu missionaries were established in Beijing and Marco Polo made his famous journey during the Yuan era. While the Chinese never accepted the Yuan as a legitimate dynasty, instead viewing them as foreign bandits, the Mongolians rebelled against the Beijing Khans for becoming, “too Chinese.†In the end, the Yuan Dynasty had the shortest duration of the major Chinese Dynasties, lasting little more than a hundred years.The term, “Cizhou,†denotes a particular type of ceramics ware. Named after the Cizhou province where examples were first unearthed, there have also been ruins of related kilns discovered in the Hebei and Henan provinces. While Cizhou ware was first created during the Five Dynasties, it only became popular during the Song and Yuan Dynasties, after which point production ceased. Cizhou wares are celebrated for their great variety of decorative motifs characterized by bold, expressive patterns with painterly qualities that can almost be called calligraphic. The free, expressive nature of Cizhou ware might be a reflection of the fact that they were created for the public and not intended for court consumption where tastes tended to be more refined. While the production of Cizhou ware was short-lived, its emphasis on decoration would affect the course of future ceramic production in China.This gorgeous, wide-bodied vase is a perfect example of the Cizhou style. While the shape of the vessel itself is quite pleasing, it is not what is emphasized. Instead, our eyes are attracted to the beautiful painted motifs that adorn this vase. The majority of the painted decoration is composed of three circular-framed areas. One is filled with a blossoming flower painted with the same freedom of brushstroke normally reserved for calligraphy and scroll painting. The other two areas depict scenes of philosopher-types contemplating the beauty of nature. No doubt the vivacity of the decoration, typical of Cizhou ware, was influenced by the constant fluctuation of nature and the changing seasons. - (H.858)
« Less
|
|
Ancient Asian
|
|
|
|
|
| Vendor Details |
Close |
| Contact Info : |
| Barakat Gallery |
| 405 North Rodeo Drive |
| Beverly Hills |
| California-90210 |
| USA |
| Email : barakat@barakatgallery.com |
| Phone : 310.859.8408 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Price :
Contact Dealer
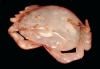
After the fall of the T’ang Dynasty, a period of unrest and war ensued, finally ending with the establishment of the Song Dynasty. The Song era was considered a time More »
After the fall of the T’ang Dynasty, a period of unrest and war ensued, finally ending with the establishment of the Song Dynasty. The Song era was considered a time of consolidation for Chinese culture. Traditional text were reanalyzed and reinterpreted, bringing forth a revival of Confucianism peppered with new ideas. Once again, civil scholars became more influential than their military counterparts. This was an era of peace, where technology and innovation flourished. Trade now focused on the seas, since the Silk Road had since been cut off. The Song viewed themselves as the culmination of two thousand years of Chinese culture. However, splinters began to emerge among the various ethnic groups that had been unified under the T’ang. As these ethnic rivalries began to grow, the government became fractured as officials began to oppose each other, allowing the Mongols from the north to invade and conquer.Although best known for their philosophical contributions, this sculpture of a crab attests to the rich artistic tradition that flourished under the enlightened rulers of the Song Dynasty. Carved from precious agate, this crab holds its claws up to its mouth as if nibbling on its latest catch. Each of the multiple legs is individually articulate, contributing to the illusion that this creature might scatter away, sideways of course. With beady, round eyes, the crab stares back at us unsure whether to run and hide or continue eating. We can picture this sculpture once decorating the imperial palace of Song Dynasty. Clearly the stunning artistry of the carving would have awed all who saw it. Likewise, finding this effigy of a sea creature inside the royal residence would have delighted the onlooker. Such a work, treasured both for its form as well as its material, would have been a luxury only afforded by the royals themselves or high-ranking officials within the court. Today, it continues to inspire us with its beauty and history that only increase with time. - (PF.6213)
« Less
|
|
Ancient Asian
|
|
|
|
|
| Vendor Details |
Close |
| Contact Info : |
| Barakat Gallery |
| 405 North Rodeo Drive |
| Beverly Hills |
| California-90210 |
| USA |
| Email : barakat@barakatgallery.com |
| Phone : 310.859.8408 |
|
|
|
|
|
|

Price :
Contact Dealer
The overextension of the labor force during the Qin Dynasty would result in a popular uprising against the empire. In 206 B.C., Liu Bang, a Qin official, led an army composed More »
The overextension of the labor force during the Qin Dynasty would result in a popular uprising against the empire. In 206 B.C., Liu Bang, a Qin official, led an army composed of peasants and some lower nobility to victory and established his own Dynasty in place, the Han. However, unlike the Qin, the Han would unify China and rule virtually uncontested for over four hundred years. It is during this time that much of what is now considered to be Chinese culture was first actualized. The bureaucracy started under the Qin was now firmly established. The vast lands of China were now under the firm grip of a central authority. Confucianism became the state ideology although the worship of Taoist deity remained widespread, both among the peasants and the aristocracy. Ancient histories and texts were analyzed and rewritten to be more objective while new legendary myths and cultural epics were transcribed.The Han era can also be characterized as one of the greatest artistic outpourings in Chinese history, easily on par with the glories of their Western contemporaries, Greece and Rome. Wealth pouring into China from trade along the Silk Road initiated a period of unprecedented luxury. Stunning bronze vessels were created, decorated with elegant inlaid gold and silver motifs. Jade carvings reached a new level of technical brilliance. But perhaps the artistic revival of the Han Dynasty is nowhere better represented than in their sculptures and vessels that were interred with deceased nobles. Called mingqi, literally meaning “spirit articles,†these works depicted a vast array of subject, from warriors and horses to ovens and livestock, which were buried alongside the dead for use in the next world, reflecting the Chinese belief that the afterlife was an extension of our earthy existence. Thus, quite logically, the things we require to sustain and nurture our bodies in this life would be just as necessary in our next life.Expressively modeled in a firm pose standing at attention with tail erect, this horse of the Han Dynasty depicts the power and grace of the new breed of horse from the west known as the "Heavenly Horse of China." This horse is caparisoned with an arrangement of ornamental harnesses and decorative bridal. Its mouth is held slightly ajar, teeth showing, and with upright ears and flared nostrils combine to imbue this work with the spirit of the steed. While the size and beauty of this horse are enough alone to impress, even more stunning is the complete carriage that this horse hauls behind him, comprised of two delicately modeled wheels, an axel rod, the carriage, and the neck yoke and poles.Considering that this sculpture was discovered buried in a tomb alongside the deceased, we can assume that the individual for who this work was created was likely carried by horse and carriage during his life as he would continue to be in the afterlife, thanks to this terracotta effigy. It is fascinating to think that this device, a horse drawn carriage, here over two-thousand years old, continued to be the major means of transportation up until the 20th century; in some parts of the world, they still are. During the reign of Emperor Wu, in order to improve the breed of horses in central China and strengthen the cavalry, the so-called "heavenly horse" was imported from the western region (present-day Middle East). Most horse sculptures found in Han Dynasty tombs portray horses with great strength and vigor. The way the horse is depicted speaks of the great love the Chinese have for the mythology and form of the horse. This horse is an expression of that affection. - (H.717) « Less
|
|
Ancient Asian
|
|
|
|
|
| Vendor Details |
Close |
| Contact Info : |
| Barakat Gallery |
| 405 North Rodeo Drive |
| Beverly Hills |
| California-90210 |
| USA |
| Email : barakat@barakatgallery.com |
| Phone : 310.859.8408 |
|
|
|
|
|
|

Price :
Contact Dealer
After almost four hundred years of civil war and division, Yang Jian succeeded in reunifying north and south under one authority, the Sui Dynasty. However, despite its brief More »
After almost four hundred years of civil war and division, Yang Jian succeeded in reunifying north and south under one authority, the Sui Dynasty. However, despite its brief duration, lasting for the rule of only two emperors, the Sui Dynasty paved the way for the cultural renaissance that would arise during the T’ang Dynasty. Reforms were introduced to wrest power out of the hands of the aristocracy, military, and Buddhist communities. The Confucianist system of selecting government officials from state schools, by means of rigorous examinations, was initiated. Perhaps their most significant program was the construction of the Great Canal, a project that facilitated the movement of people and goods across great distances, aiding in the reunification of China. However, the cost of the Canal bankrupted the empire and ultimately led to its dissolution, coupled with a failed campaign to conquer Korea. The rulers of the T’ang would capitalize on the infrastructure improvements of the Sui and establish one of the greatest empires in the history of China, following the footsteps of the Sui.Originating during the Six Dynasties period (222-589 A.D.), these types of figures are known as spirit guardians, for originally, a pair of such figures always stood guard at the tombs of Chinese rulers. Traditionally, both figures are mythological composite creatures, one always an amalgamation of various animals while the other a combination of human and animal traits. These guardians are a general type of Chinese art known as mingqi. Mingqi were any variety of objects specifically created for interment in the tombs of elite individuals in order to provide for their afterlife. These guardians were most likely interred in order to ward off potential tomb robbers or evil spirits in the next world that might try to infiltrate the tomb. This pair of spirit guardians have been decorated with an elegant crème glaze and then highlighted with red and black pigments. Both appear to have the bodies and hoofed legs of horses while one bears a human visage and the other, the fanged head of a dragon. A large spiraling horn emerges from the head of the composite dragon beast in between his ears. Black stripes along their legs enhance the animal nature of these creatures. This pair, although intending to repel us, instead attracts our gaze with their reserved, yet charming, decorations. - (H.948)
« Less
|
|
Ancient Asian
|
|
|
|
|
| Vendor Details |
Close |
| Contact Info : |
| Barakat Gallery |
| 405 North Rodeo Drive |
| Beverly Hills |
| California-90210 |
| USA |
| Email : barakat@barakatgallery.com |
| Phone : 310.859.8408 |
|
|
|
|
|
|

Price :
Contact Dealer
The T’ang Dynasty was an era of unrivalled wealth and luxury. The country was successfully reunified and the borders were expanded, pushing Chinese influence into new More »
The T’ang Dynasty was an era of unrivalled wealth and luxury. The country was successfully reunified and the borders were expanded, pushing Chinese influence into new lands. Confucianism became a semi-religious instrument of the state; yet Buddhism continued to flourish, spreading into Korea and Japan. The arts reached new levels of sophistication. Poetry and literature flourished under the enlightened rulers. The Silk Road brought fortunes into China. Precious treasures were imported on the backs of camels from far away lands and bartered for Chinese silk, medicinal herbs, and pungent spices. T’ang China was a multicultural empire where foreign merchants from across Central Asia and the Middle East settled in the urban centers, foremost among them the thriving capital of Chang’an (modern X’ian), a bustling cosmopolitan center of over two million inhabitants. Foreign traders lived next to native artisans and both thrived. New ideas and exotic artistic forms followed alongside. The T’ang Dynasty was a cultural renaissance where many of the forms and objects we now associate with China were first created. Moreover, this period represents one of the greatest cultural outpourings in human history.During the T’ang Dynasty, sculptural effigies of domesticated animals were often interred in the tombs of nobility and elite members of the social hierarchy. Created in all media, these sculptures accompanied the spirit of the deceased into the afterlife. While similar examples exist, most were found harnessed to wagons and carts and were meant to function as beasts of burden. However, this sculpture was discovered buried with other domesticated animals, suggesting that this zebu bull served as nourishment. Besides it function, this sculpture is also remarkable for its exquisite state of preservation with much of its original yellow pigment still intact. Such delicate decoration rarely survives the ravages of time and the stresses of excavation. Some of the original red pigment that also once adorned the animal is also visible on its nose. During the T’ang Dynasty, the Chinese believed that the afterlife was a continuation of our earthly existence. Thus, logically, as we require food to nourish our bodies on earth, so too will we require food to nourish our souls in the afterlife. Created to serve as food for the afterlife, this work is more than a mere sculpture; it is a gorgeous memorial to the religious and philosophical beliefs of the T’ang Dynasty. This bull effigy has served its eternal purpose well. Today, it continues to nourish our souls with its beauty and grace. - (H.945) « Less
|
|
Ancient Asian
|
|
|
|
|
| Vendor Details |
Close |
| Contact Info : |
| Barakat Gallery |
| 405 North Rodeo Drive |
| Beverly Hills |
| California-90210 |
| USA |
| Email : barakat@barakatgallery.com |
| Phone : 310.859.8408 |
|
|
|
|
|
|

Price :
Contact Dealer
Upon leading a victorious rebellion against the foreign Mongul rulers of the Yuan Dynasty, a peasant named Zhu Yuanzhang seized control of China and founded the Ming Dynasty More »
Upon leading a victorious rebellion against the foreign Mongul rulers of the Yuan Dynasty, a peasant named Zhu Yuanzhang seized control of China and founded the Ming Dynasty in 1368. As emperor, he founded his capital at Nanjing and adopted the name Hongwu as his reign title. Hongwu, literally meaning “vast military,†reflects the increased prestige of the army during the Ming Dynasty. Due to the very realistic threat still posed by the Mongols, Hongwu realized that a strong military was essential to Chinese prosperity. Thus, the orthodox Confucian view that the military was an inferior class to be ruled over by an elite class of scholars was reconsidered. During the Ming Dynasty, China proper was reunited after centuries of foreign incursion and occupation. Ming troops controlled Manchuria, and the Korean Joseon Dynasty respected the authority of the Ming rulers, at least nominally.Like the founders of the Han Dynasty (206 B.C.- 220 A.D.), Hongwu was extremely suspicious of the educated courtiers that advised him and, fearful that they might attempt to overthrow him, he successfully consolidated control of all aspect of government. The strict authoritarian control Hongwu wielded over the affairs of the country was due in part to the centralized system of government he inherited from the Monguls and largely kept intact. However, Hongwu replaced the Mongul bureaucrats who had ruled the country for nearly a century with native Chinese administrators. He also reinstituted the Confucian examination system that tested would-be civic officials on their knowledge of literature and philosophy. Unlike the Song Dynasty (960-1279 A.D.), which received most of its taxes from mercantile commerce, the Ming economy was based primarily on agriculture, reflecting both the peasant roots of its founder as well as the Confucian belief that trade was ignoble and parasitc.Culturally, the greatest innovation of the Ming Dynasty was the introduction of the novel. Developed from the folk tales of traditional storytellers, these works were transcribed in the everyday vernacular language of the people. Advances in printmaking and the increasing population of urban dwellers largely contributed to the success of these books. Architecturally, the most famous monument of the Ming Dynasty is surely the complex of temples and palaces known as the Forbidden City that was constructed in Beijing after the third ruler of the Ming Dynasty, Emperor Yongle, moved the capital there. Today, the Forbidded Palace remains one of the hallmarks of traditional Chinese architecture and is one of the most popular tourist destinations in the vast nation.Ming statuette art reflects the attempt to restore purely “Chinese†artistic genres with a healthy injection of Confucian aesthetic, political, and moral standards. Realistic depictions of daily life became popular themes among artists who were often patronized by the court. Under Xuande's reign (1426-35), the art industry flourished, producing many exquisite porcelain and ceramic pieces. This glazed set is a product of the artistic revival that occurred throughout the Ming. This Ming set of glazed figurines depicts an aspect of Chinese political and social life. Tributary processions were common protocol at this time, the emperor requiring provincial lords to pay tribute and tax on a regular basis. Processions were also held for funerals, marriages, and rituals differing in grandeur depending on the status of the individuals involved and nature of the ceremony. The palanquin served as the primary form of transportation for the elite who often traveled with several attendants.This extraordinary tomb find consists of ten horse and rider sculptures, thirty-eight individual attendants, and two palanquins. The horse march forward, followed by a retinue of attendants, both male and female, presenting a range of presents. Finally, the procession would culminate with the palanquins that were once held aloft on wooden poles, carried on the shoulders of the attendants, which have long since deteriorated. The palanquins are naturally empty, for they were meant to carry the deceased nobility alongside whom they were buried into the afterlife. As Chinese statuette art prescribes, the faces are created individually with uniquely painted features, owing to their distinctive expressions. The pieces still retain much of their original polychrome paint, remarkable considering the stresses of excavation and the delicate nature of the pigment. Evidence of gilding is still visible on a large plate carried by one of the ladies in waiting. One of the riders wears a stunning yellow and black tunic that appear to have been made from the hide of a tiger. This astounding set is a masterpiece of Ming art, not just for the size of the procession and the diversity of the poses and gestures, but also for the remarkable preservation of the original details and the beauty of each piece as an individual work of art and united together as masterpiece. - (H.962) « Less
|
|
Ancient Asian
|
|
|
|
|
| Vendor Details |
Close |
| Contact Info : |
| Barakat Gallery |
| 405 North Rodeo Drive |
| Beverly Hills |
| California-90210 |
| USA |
| Email : barakat@barakatgallery.com |
| Phone : 310.859.8408 |
|
|
|
|
|
|

Price :
Contact Dealer
The overextension of the labor force during the Qin Dynasty would result in a popular uprising against the empire. In 206 B.C., Liu Bang, a Qin official, led an army composed More »
The overextension of the labor force during the Qin Dynasty would result in a popular uprising against the empire. In 206 B.C., Liu Bang, a Qin official, led an army composed of peasants and some lower nobility to victory and established his own Dynasty in place, the Han. However, unlike the Qin, the Han would unify China and rule virtually uncontested for over four hundred years. It is during this time that much of what is now considered to be Chinese culture was first actualized. The bureaucracy started under the Qin was now firmly established. The vast lands of China were now under the firm grip of a central authority. Confucianism became the state ideology although the worship of Taoist deity remained widespread, both among the peasants and the aristocracy. Ancient histories and texts were analyzed and rewritten to be more objective while new legendary myths and cultural epics were transcribed.The Han era can also be characterized as one of the greatest artistic outpourings in Chinese history, easily on par with the glories of their Western contemporaries, Greece and Rome. Wealth pouring into China from trade along the Silk Road initiated a period of unprecedented luxury. Stunning bronze vessels were created, decorated with elegant inlaid gold and silver motifs. Jade carvings reached a new level of technical brilliance. But perhaps the artistic revival of the Han Dynasty is nowhere better represented than in their sculptures and vessels that were interred with deceased nobles. Called mingqi, literally meaning “spirit articles,†these works depicted a vast array of subject, from warriors and horses to ovens and livestock, which were buried alongside the dead for use in the next world, reflecting the Chinese belief that the afterlife was an extension of our earthy existence. Thus, quite logically, the things we require to sustain and nurture our bodies in this life would be just as necessary in our next life.The Han Dynasty, like the Zhou before it, is divided into two distinct periods, the Western Han (206 B.C.-9 A.D.) and the Eastern Han (23-220 A.D.) with a brief interlude. Towards the end of the Western period, a series of weak emperors ruled the throne, controlled from behind the scenes by Wang Mang and Huo Guang, both relatives of empresses. They both exerted enormous influence over the government and when the last emperor suddenly passed away, Mang became ruling advisor, seizing this opportunity to declare his own Dynasty, the Xin, or “New.†However, another popular uprising began joined by the members of the Liu clan, the family that ruled the Han Dynasty, the Xin came to a quick end and the Eastern Han was established in its place with its capital at Loyang (Chang’an, the capital of the Western Han, was completely destroyed).However, even as Chinese influence spread across Southeastern Asia into new lands, the Eastern Han Dynasty was unable to recreate the glories of the Western Period. In fact, this period can be characterized by a bitter power struggle amongst a group of five consortial clans. These families sought to control the young, weak emperors with their court influence. Yet, as the emperors became distrustful of the rising power of the clans, they relied upon their eunuchs to defend them, often eliminating entire families at a time. During the Western Han, the Emperor was viewed as the center of the universe. However, this philosophy slowly disintegrated under the weak, vulnerable rulers of the Eastern Han, leading many scholars and officials to abandon the court. Eventually, the power of the Han would completely erode, ending with its dissolution and the beginning of the period known as the “Three Kingdoms.â€Striding forward on powerful haunches, this mythological beast is a composite of several different animals. He bears the hoofed legs and muscular body of a bull with a distinctively bovine head. Bosses rise from his body, following his spinal chord, and culminate in two pointed horns that protrude from the top of his neck. His arched tail, held up over his back, appears to be more canine that bovine or equestrian. Might this beast be a fanciful depiction of a dragon? Certainly the horns and head suggest so. Clearly, this is a fierce, untamed beast. With its head lowered, he appears to charge forward like a pull, thrusting his horns forward into whatever obstacle might block his path. His ribcage is visible along his torso, imbuing the work with energy and vitality. This magnificent sculpture is an insightful glimpse into the fantastic mythology of ancient China. - (H.917)
« Less
|
|
Ancient Asian
|
|
|
|
|
| Vendor Details |
Close |
| Contact Info : |
| Barakat Gallery |
| 405 North Rodeo Drive |
| Beverly Hills |
| California-90210 |
| USA |
| Email : barakat@barakatgallery.com |
| Phone : 310.859.8408 |
|
|
|
|
|
|

Price :
Contact Dealer
The T’ang Dynasty was an era of unrivalled wealth and luxury. The country was successfully reunified and the borders were expanded, pushing Chinese influence into new More »
The T’ang Dynasty was an era of unrivalled wealth and luxury. The country was successfully reunified and the borders were expanded, pushing Chinese influence into new lands. Confucianism became a semi-religious instrument of the state; yet Buddhism continued to flourish, spreading into Korea and Japan. The arts reached new levels of sophistication. Poetry and literature flourished under the enlightened rulers. The Silk Road brought fortunes into China. Precious treasures were imported on the backs of camels from far away lands and bartered for Chinese silk, medicinal herbs, and pungent spices. T’ang China was a multicultural empire where foreign merchants from across Central Asia and the Middle East settled in the urban centers, foremost among them the thriving capital of Chang’an (modern X’ian), a bustling cosmopolitan center of over two million inhabitants. Foreign traders lived next to native artisans and both thrived. New ideas and exotic artistic forms followed alongside. The T’ang Dynasty was a cultural renaissance where many of the forms and objects we now associate with China were first created. Moreover, this period represents one of the greatest cultural outpourings in human history.During the Tang Dynasty, restrictions were placed on the number of objects that could be included in tombs, an amount determined by an individual's social rank. In spite of the limitations, a striking variety of tomb furnishings have been excavated. Entire retinues of ceramic figures - animals, entertainers, musicians, guardians - were buried with the dead. Many of the objects reflect Tang China's extraordinary amount of contact with foreigners, bringing into China influences that were then adapted and absorbed into its culture. One of these influences is apparent in this figure that corresponds to Buddhist warrior deities that assume a mortuary role in China but also serve as protectors of Buddhist temples. Known as "Protector of the Burial Vault" or "Protector of the Burial Ground," the fierce, this armored guardian stands atop a grotesque demon. This stance symbolizes the heavenly king's authority and responsibility as protector of the tomb.A remarkable amount of this sculpture’s original pigment has survived the ravages of time intact, perhaps most visible in the spectacular vibrant red, orange, and green floral decorations that adorn his armor. Traces of the gilding are also visible, attesting to the luxurious nature of this sculpture. According to one Chinese tradition explaining their origin, Emperor Taizong, when ill, was threatened by ghosts outside of his room screeching and throwing bricks and tiles. When his general Jin Shubao (Chin Shu-pao) and a fellow officer came to stand guard the activity of the ghosts ceased. The grateful emperor had portraits of the two men hung on either side of his palace gates, and thereafter their images became widespread as door-gods. Originally, he would have brandished a weapon fabricated in a material such as wood that has deteriorated over the centuries. Looking unto his stern face and flaming hair and gazing into his fierce eyes, we understand why such works were intended to frighten away tomb robbers and evil spirits. Yet despite his intimidating nature, he does not repel us; instead, we are attracted to his artistic mastery and intriguing history. - (H.925) « Less
|
|
Ancient Asian
|
|
|
|
|
| Vendor Details |
Close |
| Contact Info : |
| Barakat Gallery |
| 405 North Rodeo Drive |
| Beverly Hills |
| California-90210 |
| USA |
| Email : barakat@barakatgallery.com |
| Phone : 310.859.8408 |
|
|
|
|
|
|

Price :
Contact Dealer
The T’ang Dynasty was an era of unrivalled wealth and luxury. The country was successfully reunified and the borders were expanded, pushing Chinese influence into new More »
The T’ang Dynasty was an era of unrivalled wealth and luxury. The country was successfully reunified and the borders were expanded, pushing Chinese influence into new lands. Confucianism became a semi-religious instrument of the state; yet Buddhism continued to flourish, spreading into Korea and Japan. The arts reached new levels of sophistication. Poetry and literature flourished under the enlightened rulers. The Silk Road brought fortunes into China. Precious treasures were imported on the backs of camels from far away lands and bartered for Chinese silk, medicinal herbs, and pungent spices. T’ang China was a multicultural empire where foreign merchants from across Central Asia and the Middle East settled in the urban centers, foremost among them the thriving capital of Chang’an (modern X’ian), a bustling cosmopolitan center of over two million inhabitants. Foreign traders lived next to native artisans and both thrived. New ideas and exotic artistic forms followed alongside. The T’ang Dynasty was a cultural renaissance where many of the forms and objects we now associate with China were first created. Moreover, this period represents one of the greatest cultural outpourings in human history.During the Tang Dynasty, restrictions were placed on the number of objects that could be included in tombs, an amount determined by an individual's social rank. In spite of the limitations, a striking variety of tomb furnishings, known as mingqi, have been excavated. Entire retinues of ceramic figures - animals, entertainers, musicians, guardians - were buried with the dead in order to provide for the afterlife. Of the various types of mingqi, there is perhaps none more beautiful or charming than the sculptures of elegant female courtiers. These gorgeous sculptures represent the idealized woman of T’ang Dynasty China. This sculpture representing such a sophisticated lady is remarkable for its size, nearly twice as large as the standard type. She provided eternal companionship for her lord throughout the afterlife. We can imagine her gracefully dancing or singing a poetical song, two very popular customs for ladies during the T’ang Dynasty, considered a golden age of Chinese culture. Such courtiers are described in the numerous love poems written during this era, likely the greatest outpouring of poetry in Chinese history.She wears her hair in an elegant coiffure featuring two buns that appears almost like the alert ears of a startled dog. This elaborate hairstyle is matched by her sumptuous orange robe. Much of the original pigment that once decorated this work remains intact, most noticeable in her dress, her vibrant red lips, and her soft, rosy cheeks. Such women may represent wives, princesses, or attendants. She carries what appears to be a flower-shaped loaf of bread or some pastry treat, pointing to it with her other hand as she proudly presents it to us. Their beauty inspires us as we are transported back to another time. This large terracotta effigy of an ancient courtier has been to the next world and returned to our modern era to tell us her tale. She speaks of the enormous wealth and sophisticated culture of the T’ang Dynasty, one of the greatest periods of artistic creation in human history. Although she speaks of the past, this lady in waiting continues to amaze us in the present with her unmatched beauty and sculptural refinement. - (H.997)
« Less
|
|
Ancient Asian
|
|
|
|
|
| Vendor Details |
Close |
| Contact Info : |
| Barakat Gallery |
| 405 North Rodeo Drive |
| Beverly Hills |
| California-90210 |
| USA |
| Email : barakat@barakatgallery.com |
| Phone : 310.859.8408 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|


